
How to Reduce the Risk of RSI in 384-well Applications
Lab Academy
- Health & Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Efficiency
- Quality
- Reproducibility
- Ergonomics
- Accuracy
- Pipette Tips
- Essay
With the advent of the high-throughput screening approach, the need for a microplate with a larger number of wells appeared and was quickly implemented as a consumable for plate assays. Applications performed in 384-well plates require repetitive liquid handling steps. Automated pipetting platforms represent an investment that smaller labs or companies often cannot afford. Then multi-channel pipettes are preferred. Thus, 16 or 24-channel pipettes designed to fit the 384-well microplate format are an alternative solution for scientists looking to increase their throughput. Compared to 8 or 12-channel pipettes, especially the electronic versions of 16 or 24-channel pipettes save pipetting time and reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs).
Reducing the number of arm movements help minimize the risk of RSI
- Using multichannel pipettes instead of single-channel pipettes - if available 16 or 24-channel pipettes
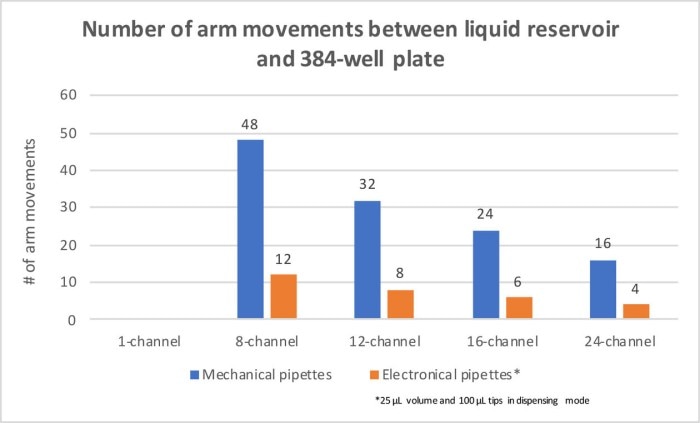
a. For instance, arm movement can be reduced from 48 movements with an 8-channel pipette to 16 movements with a 24-channel pipette (=> reduces arm movement by 67%) - The use of multichannel electronic pipettes in dispensing mode further reduces arm movement significantly, as shown in Figure 1.
- The use of electronic 24-channel pipettes in dispensing mode represents the ultimate solution as only between 1 and 16 arm movements are needed, depending on the volume used.
a. For instance, when dispensing a volume of 25 µL with a 100 µL tip, 4 arm movements are needed per plate, saving additional 75% compared to 16 movements with mechanical 24-channel pipettes
b. Thus, compared to mechanical 8-channel pipettes you can save 92% of arm movements with electronic 24-channel pipette in dispensing mode
In summary, a higher number of channels has a direct impact on the number of movements required to dispense liquids into plates. With a 16 or 24-channel pipette, the number of movements is decreased, especially with electronic models used in dispensing mode, reducing significantly the risk of repetitive strain injury appearance.
